Traveling often exposes individuals to heightened risks of identity theft due to increased reliance on public Wi-Fi and the potential for device loss. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as an effective defense mechanism against these threats. By requiring multiple verification methods, MFA fortifies account security. Understanding how MFA operates and its implementation can greatly enhance one’s digital safety. However, understanding how multi-factor authentication enhances security and implementing it into everyday travel routines remains essential.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds layers of verification, making unauthorized access to accounts more difficult during travel.
- MFA combines something you know (password) with something you have (mobile device), enhancing security against identity theft.
- Unusual access attempts can trigger additional authentication prompts, providing an extra layer of protection while traveling.
- Implementing MFA on sensitive accounts safeguards personal data even if devices are lost or stolen while on the road.
- Using MFA as part of travel security practices helps mitigate risks associated with public Wi-Fi vulnerabilities and phishing attacks.
Understanding the Risks of Identity Theft While Traveling
How can travelers effectively safeguard their personal information in an increasingly interconnected world? Understanding the risks of identity theft while traveling is vital for ensuring personal security. Travelers often utilize public Wi-Fi networks, which are inherently insecure, making them vulnerable to data breaches. Additionally, lost or stolen devices can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information. Phishing attacks can also occur through seemingly legitimate communications. Travelers should be aware that their personal data is at risk not only from cyber threats but also from physical theft. To mitigate these risks, implementing robust security measures, such as using strong, unique passwords and being vigilant about the information shared online, is essential. Ultimately, understanding these risks empowers travelers to protect their identities effectively.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
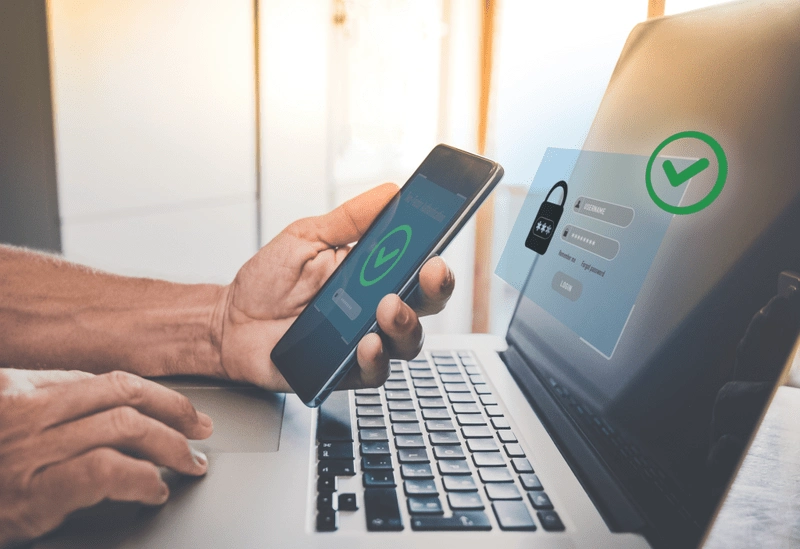
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as a critical layer of security that enhances the protection of personal information in an increasingly digital landscape. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to an account or system. This typically involves a combination of something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (such as a smartphone or security token), and something the user is (biometric data like fingerprints). By implementing MFA, organizations can considerably reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access, as it creates additional barriers for potential intruders. As cyber threats continue to evolve, understanding and utilizing MFA is essential for individuals seeking to safeguard their sensitive information while maintaining a sense of community in the digital world.
How Multi-Factor Authentication Enhances Security
Implementing a robust security framework is essential for protecting sensitive information in today’s digital environment. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors before granting access to accounts. This method greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as it combines something the user knows (password) with something the user has (a mobile device or security token). Even if a password is compromised, the additional verification steps serve as a substantial barrier against identity theft. In addition, MFA can adapt to user behavior, triggering requests for additional authentication during unusual access attempts. By integrating MFA, individuals and organizations can foster a more secure digital environment, ensuring their information remains safeguarded while traveling or conducting online activities.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication for Your Accounts
Adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an essential step in enhancing account security. To implement MFA, individuals should begin by evaluating the accounts that hold sensitive information, such as email, banking, and social media. Most platforms offer MFA options, typically involving a combination of something the user knows (password) and something the user has (a mobile device or hardware token). Users must navigate to the security settings of their accounts and enable MFA, following the prompts to link their mobile device for verification codes. Regularly updating recovery options and ensuring that backup methods are secure also fortifies protection. Ultimately, implementing multi-factor authentication for your accounts greatly reduces the risk of identity theft, providing a robust layer of security while traveling.
Best Practices for Safe Travel in the Digital Age
How can travelers guarantee their personal information remains secure in an increasingly digital world? Adopting best practices is essential for safeguarding digital safety while on the move. Travelers must prioritize strategies to mitigate risks associated with identity theft.
- Utilize multi-factor authentication for all accounts to enhance security.
- Regularly update passwords and verify they are complex and unique.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions; instead, opt for a VPN.
- Keep data backed up and accessible in a secure manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Devices Support Multi-Factor Authentication?
Various devices support multi-factor authentication, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and hardware tokens. These devices enhance security by requiring multiple verification methods, thereby greatly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and identity theft in digital environments.
Is Multi-Factor Authentication Free to Use?
Multi-factor authentication is often free to use and available through various online services. Users typically access it via their accounts without additional costs, enhancing security and fostering a sense of community among users prioritizing safety.
Can I Use Multi-Factor Authentication Offline?
Multi-factor authentication typically requires an internet connection for verification, yet some methods, like hardware tokens or SMS codes received prior, can provide offline access. Understanding how multi-factor authentication enhances security is essential for effective protection strategies.
How Often Should I Update My Authentication Methods?
Updating authentication methods should occur regularly, ideally every three to six months. This practice guarantees enhanced security, adapting to evolving threats while fostering a sense of community among users who prioritize their digital safety.
Are There Exceptions to Using Multi-Factor Authentication?
Exceptions to using multi-factor authentication may arise in scenarios involving legacy systems, user accessibility issues, or environments where technology restrictions exist. Nevertheless, implementing multi-factor authentication enhances security, mitigating risks associated with identity theft effectively.
Conclusion
To summarize, multi-factor authentication serves as a crucial defense mechanism against identity theft while traveling. By requiring multiple verification methods, it greatly mitigates the risks associated with unauthorized access to sensitive accounts. As travelers increasingly rely on digital platforms, implementing MFA across various accounts is necessary for enhancing security. Adopting best practices for safe travel in the digital age, combined with the robust protection offered by MFA, provides an all-encompassing approach to safeguarding personal information from cyber threats.
You May Also Like To Read:





